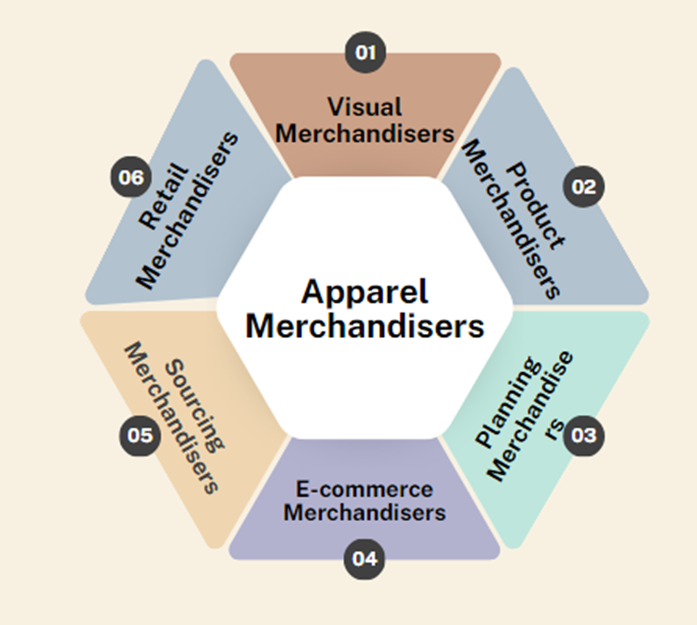
The Classification of Garments Merchandisers
In the apparel industry, merchandisers play a pivotal role in ensuring that the right products are available to consumers at the right time and in the right place. Understanding the different classifications of garments merchandisers can help businesses optimize their supply chains, improve product offerings, and enhance customer satisfaction. In this blog, we will explore the various types of apparel merchandisers, their roles, and how they contribute to the fashion industry. Lets discuss more about Classification of garments Merchandisers.
Classification of Garments Merchandisers
Apparel merchandisers can be broadly classified into several categories based on their specific functions and responsibilities. The primary classifications of garments merchandisers include:
- Retail Merchandisers
- Visual Merchandisers
- Product Merchandisers
- Planning Merchandisers
- Sourcing Merchandisers
- E-commerce Merchandisers
Flow Chart of Apparel Merchandisers
Below is a flow chart illustrating the different types of apparel merchandisers and their primary functions:

Detailed Classification
1. Retail Merchandisers
Retail merchandisers focus on the physical presence of apparel products in stores. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Inventory Management: Ensuring adequate stock levels.
- Sales Analysis: Monitoring sales data to adjust inventory and promotions.
- Store Layout: Optimizing product placement to enhance the shopping experience.
2. Visual Merchandisers
Visual merchandisers specialize in the aesthetic presentation of apparel products to attract and engage customers. Key tasks include:
- Window Displays: Designing eye-catching window displays.
- In-Store Displays: Creating appealing in-store product arrangements.
- Brand Image: Ensuring displays align with the brand’s image and messaging.
3. Product Merchandisers
Product merchandisers are responsible for developing and managing the product line. Their duties involve:
- Product Development: Collaborating with designers and manufacturers.
- Quality Control: Ensuring products meet quality standards.
- Pricing Strategy: Setting competitive pricing.
4. Planning Merchandisers
Planning merchandisers focus on forecasting and planning inventory needs. Their primary tasks include:
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future sales trends.
- Inventory Planning: Aligning inventory levels with forecasted demand.
- Budget Management: Managing budgets for inventory procurement.
5. Sourcing Merchandisers
Sourcing merchandisers manage the procurement of raw materials and finished goods. Their responsibilities include:
- Supplier Selection: Identifying and vetting suppliers.
- Cost Negotiation: Negotiating prices with suppliers.
- Logistics Coordination: Managing the logistics of shipping and delivery.
6. E-commerce Merchandisers
E-commerce merchandisers focus on online retail platforms. Their key responsibilities are:
- Website Management: Ensuring the online store is user-friendly and updated.
- Digital Marketing: Implementing online marketing strategies.
- Analytics: Analyzing web traffic and sales data to optimize the online shopping experience.
This Merchandiser can also be classified in 3 more categories.
- Fashion Merchandiser
- Export Merchandiser
- Retail Merchandiser

1. What is a Fashion Merchandiser?
A fashion merchandiser is a professional who works in the retail and fashion sectors to plan, develop, and present fashion lines and products. They balance creativity with business acumen, ensuring that fashion items appeal to consumers while meeting sales and profitability goals.
Key Responsibilities of a Fashion Merchandiser
- Market Research:
- Conducting research to understand market trends, consumer preferences, and competitor activities.
- Analyzing data to forecast future fashion trends and demands.
2. Product Development:
- Collaborating with designers to create appealing and marketable fashion items.
- Ensuring products meet quality standards and are produced within budget.
3. Inventory Management:
- Managing stock levels to ensure adequate supply without overstocking.
- Coordinating with suppliers and manufacturers to streamline the supply chain.
4. Sales Analysis:
- Monitoring sales data to identify best-selling items and underperforming products.
- Adjusting merchandising strategies based on sales performance.
5. Pricing Strategy:
- Setting competitive prices to attract consumers while maintaining profitability.
- Implementing discount strategies and promotions to boost sales.
6. Visual Merchandising:
- Designing store layouts and displays to enhance the shopping experience.
- Ensuring visual presentations align with the brand’s image and marketing strategies.
7. Marketing Coordination:
- Working with marketing teams to develop campaigns that promote fashion lines.
- Utilizing social media and other digital platforms to reach target audiences.
Essential Skills for a Fashion Merchandiser
- Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze market trends, sales data, and consumer behavior to make informed decisions.
- Creativity: Designing appealing product displays and collaborating on product development.
- Communication Skills: Effectively communicating with designers, suppliers, and marketing teams.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring products meet quality standards and are correctly priced and displayed.
- Business Acumen: Understanding financial aspects, including budgeting, pricing strategies, and sales analysis.
The Impact of a Fashion Merchandiser
A fashion merchandiser significantly impacts a brand’s success by:
- Driving Sales: Through effective product placement, pricing strategies, and marketing efforts.
- Enhancing Brand Image: By ensuring products and displays reflect the brand’s identity and appeal to the target market.
- Optimizing Inventory: Balancing stock levels to meet consumer demand without overstocking.
- Increasing Profitability: By selecting products that meet market demand and managing costs effectively.
2. What is an Export Merchandiser?
An export merchandiser is a professional who specializes in handling the export of goods from one country to another. They work closely with manufacturers, buyers, and logistics companies to manage the entire export process, ensuring that products meet international standards and reach their destinations on time.
Key Responsibilities of an Export Merchandiser
- Order Management:
- Processing and managing orders from international buyers.
- Coordinating with suppliers to ensure timely production and shipment.
2. Quality Control:
- Ensuring that products meet the required quality standards and specifications of the buyer.
- Conducting inspections and overseeing quality assurance processes.
3. Documentation:
- Preparing and managing all necessary export documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Ensuring compliance with international trade regulations and customs requirements.
4. Logistics Coordination:
- Arranging transportation and shipping logistics to ensure timely delivery.
- Working with freight forwarders and shipping companies to optimize shipping routes and costs.
5. Cost Management:
- Negotiating prices with suppliers and buyers to ensure competitive pricing.
- Managing budgets and ensuring cost-effective export operations.
6. Market Research:
- Analyzing international market trends and identifying potential new markets for export.
- Keeping abreast of changes in trade regulations and tariffs.
7. Customer Communication:
- Maintaining regular communication with international buyers to update them on order status and resolve any issues.
- Building and maintaining strong relationships with customers to foster long-term business.
Essential Skills for an Export Merchandiser
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring accuracy in documentation and quality control.
- Communication Skills: Effectively communicating with buyers, suppliers, and logistics providers.
- Organizational Skills: Managing multiple orders and coordinating complex logistics.
- Analytical Skills: Analyzing market trends and cost data to make informed decisions.
- Negotiation Skills: Negotiating prices and terms with suppliers and buyers.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding and respecting cultural differences in international trade.
The Impact of an Export Merchandiser
An export merchandiser plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods from one country to another, significantly impacting a company’s success in global markets. Their contributions include:
- Timely Deliveries: Coordinating efficient logistics to meet delivery deadlines.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that products meet international quality standards.
- Cost Efficiency: Managing costs to maintain profitability in international trade.
- Market Expansion: Identifying and tapping into new international markets.
3. What is a Retail Merchandiser?
A retail merchandiser is a professional who manages the product displays and inventory within retail stores. They work closely with store managers, buyers, and marketing teams to create an appealing shopping environment that encourages customers to make purchases.
Key Responsibilities of a Retail Merchandiser
- Product Placement:
- Strategically placing products to maximize visibility and sales.
- Ensuring that high-demand items are easily accessible to customers.
2. Inventory Management:
- Monitoring stock levels and replenishing inventory as needed.
- Coordinating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of products.
3. Sales Analysis:
- Analyzing sales data to identify trends and adjust merchandising strategies.
- Monitoring the performance of different product lines and making recommendations for adjustments.
4. Store Layout Design:
- Designing and implementing store layouts that enhance the shopping experience.
- Creating attractive and engaging product displays.
5. Promotion Planning:
- Developing and implementing promotional strategies to boost sales.
- Coordinating with marketing teams to execute in-store promotions and events.
6. Customer Insights:
- Gathering and analyzing customer feedback to improve product placement and store layout.
- Staying informed about consumer preferences and shopping behaviors.
Essential Skills for a Retail Merchandiser
- Creativity: Designing appealing product displays and store layouts.
- Analytical Skills: Analyzing sales data and market trends to make informed decisions.
- Communication Skills: Effectively communicating with store managers, suppliers, and marketing teams.
- Organizational Skills: Managing inventory and coordinating multiple tasks.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring products are displayed neatly and accurately.
- Customer Focus: Understanding and meeting the needs and preferences of customers.
The Impact of a Retail Merchandiser
A retail merchandiser significantly impacts a store’s success by:
- Increasing Sales: Effective product placement and promotional strategies can drive sales and boost revenue.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Attractive displays and well-organized stores create a pleasant shopping environment.
- Optimizing Inventory: Efficient inventory management ensures that popular items are always in stock.
- Improving Store Performance: Analyzing sales data helps identify areas for improvement and implement effective changes.
Comparative Analysis: Export Merchandiser vs. Domestic Merchandiser
| Aspect | Export Merchandiser | Domestic Merchandiser |
| Market Focus | International markets | Domestic markets |
| Documentation | Extensive export documentation required | Limited to local trade documentation |
| Logistics Complexity | High, involving international shipping | Lower, involving domestic transportation |
| Regulatory Compliance | Must comply with international trade laws | Complies with domestic trade regulations |
| Cultural Awareness | High, understanding diverse cultures | Moderate, focuses on local market |
Comparative Analysis: Fashion Merchandiser vs. Other Merchandisers
| Aspect | Fashion Merchandiser | Other Merchandisers |
| Focus Area | Fashion and apparel products | Can vary (electronics, groceries, etc.) |
| Creativity Level | High, involves trend forecasting and visual merchandising | Medium to high, depending on product category |
| Market Research | In-depth analysis of fashion trends | Focused on specific product trends |
| Collaboration | Works closely with designers and marketing teams | Works with product managers and suppliers |
| Sales Analysis | Monitors fashion sales and consumer preferences | Analyzes sales for various product categories |
Comparative Table of Apparel Merchandisers
| Merchandiser Type | Primary Function | Key Responsibilities |
| Retail Merchandisers | Physical store management | Inventory management, sales analysis, store layout |
| Visual Merchandisers | Aesthetic product presentation | Window displays, in-store displays, maintaining brand image |
| Product Merchandisers | Product line development and management | Product development, quality control, pricing strategy |
| Planning Merchandisers | Inventory forecasting and planning | Demand forecasting, inventory planning, budget management |
| Sourcing Merchandisers | Procurement of materials and goods | Supplier selection, cost negotiation, logistics coordination |
| E-commerce Merchandisers | Online retail platform management | Website management, digital marketing, web analytics |
Takeaway
Understanding the classification of apparel merchandisers is crucial for optimizing operations within the fashion industry. Each type of merchandiser plays a unique role, from managing physical stores and creating visual displays to developing products and overseeing online platforms. By recognizing the distinct functions and responsibilities of these merchandisers, businesses can better align their strategies to meet consumer demands and achieve greater success in the competitive apparel market.
For more insights into the apparel industry and effective merchandising strategies, stay tuned to our blog!